Telerik was founded in Bulgaria.
We can get a rough estimate of their relative popularity by checking the Tags in StackOverflow:


using System; public class Animal { public string repColor = "brown"; } public class Reptile: Animal { string repColor = "green"; public void display() { Console.WriteLine("Color: "+base.repColor); Console.WriteLine("Color: "+repColor); } } public class Demo { public static void Main() { Reptile rep = new Reptile(); rep.display(); } }
Color: brown Color: green
 Interface and Abstract class both contribute to “incomplete type” in OOP. Sometimes we need a superclass to define “what to do” but, not “how to do”, it’s how to do part will be implemented by the derived class according to its need, “interface” provide a solution to this. Sometimes we need a superclass class that defines some generalised structure that can be implemented by derived classes and some specified structure that can be utilised by the derived classes, “abstract class” provides a solution to this. The fundamental difference between interface and abstract class is that interface is fully incomplete, and abstract class is partially incomplete.
Interface and Abstract class both contribute to “incomplete type” in OOP. Sometimes we need a superclass to define “what to do” but, not “how to do”, it’s how to do part will be implemented by the derived class according to its need, “interface” provide a solution to this. Sometimes we need a superclass class that defines some generalised structure that can be implemented by derived classes and some specified structure that can be utilised by the derived classes, “abstract class” provides a solution to this. The fundamental difference between interface and abstract class is that interface is fully incomplete, and abstract class is partially incomplete.| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | INTERFACE | ABSTRACT CLASS |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | When you only have the knowledge of the requirements not about its implementation, you use "Interface". | When you partially know about the implementations you use "Abstract classes". |
| Methods | Interface only contains abstract methods. | Abstract class contains abstract methods as well as concrete methods. |
| Access Modifier of Methods | Interface methods are always "Public" and "Abstract", even if we do not declare. Hence, it can be said as 100%, pure abstract class. | It is not compulsory that method in abstract class will be public and abstract. It can have concrete methods also. |
| Restricted Modifier for Methods | An interface method can not be declared with the following modifiers: Public: Private and Protected Abstract: final, static, synchronized, native, strictfp. | There are no restrictions on the modifiers of the abstract class variable. |
| Access Modifier of Variables | Acess Modifier allowed for Interface variables are public, static & final whether we are declaring or not. | The variables in abstract class need not be public, static, final. |
| Restricted modifiers for Variables | Interface variables can not be declared as private, protected, transient, volatile. | There is no restriction on the modifiers of abstract class variables. |
| Initialization of variables | The interface variables must be initialized at the time of its declaration. | It is not compulsory that abstract class variables must be initialized at the time of its declaration. |
| Instance and static blocks | Inside interface, you can't declare an instance or static block. | Abstract class allows an instance or static block inside it. |
| Constructors | You can not declare constructor inside interface. | You can declare constructor inside an abstract class. |
Definition of Interface
Java doesn’t allow multiple inheritance. That is, a single class cannot inherit more than one class at a time. The reason behind this can be explained with an example. Let’s suppose we have two parent class, A and B and a derived class C. The derived class C inherits both the classes A and B. Now, both have the class A and B have method set( ), then it will be a question for class C that which class’s set( ) method should it inherit. The solution to this problem is “interface”.
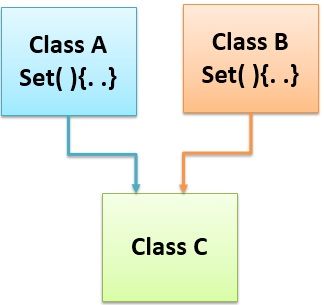 Interface is a pure abstract class. The keyword used to create an interface is “interface”. As all the method inside interface are fully abstract. The interface only specifies what a class must do but, it does not define how it does it. Just because all the method declared inside the interface are abstract, no instance is created for an interface. The general form of “interface” in java is: Interface is a pure abstract class. The keyword used to create an interface is “interface”. As all the method inside interface are fully abstract. The interface only specifies what a class must do but, it does not define how it does it. Just because all the method declared inside the interface are abstract, no instance is created for an interface. The general form of “interface” in java is:
The access specifier is declared public because the classes need to implement the interface.
We do not have the concept of “Interface” in C++. But, Java and C# define interface very well.
Interface in Java:
The general form of implementing an interface in Java:
For inheriting an interface, a class uses a keyword “implements”, and the class implements all the method declared by an inherited interface.
Interface in C#:
Interface in C# are almost similar to interface in Java except:
The general form of implementing an interface in C#:
Definition of Abstract Class
A class that contains one or more abstract methods is called abstract class, and a class is declared as abstract using the keyword “abstract”, preceded by the “class” keyword at the beginning of the class declaration. As the abstract class contains the abstract method it constitutes to an incomplete type. Hence, you can not create objects of an abstract class. Whenever a class inherits an abstract class, it must implement all the abstract methods of the abstract class if it doesn’t then it must also be declared as abstract.The abstract attribute is inherited until the complete implementation of abstract methods is achieved.
The abstract class can also contain concrete methods which can be utilised by the derived class as it is. But, you can not declare an abstract constructor or an abstract static method inside an abstract class. The general form of the abstract class in Java is as follow:
The concept of an abstract class is similar in both Java and C#. An abstract class is slightly different in C++.
In C++ if a class at least have one virtual function the class becomes an abstract class. Instead of the keyword “abstract”, the keyword “virtual” is used to declare an abstract method.
Key Differences Between Interface and Abstract Class in Java & C#
Conclusion:
When you need to create a base class which contains a generalised form of methods that can be implemented by the derived classes according to their need, the concept of interface and abstract class helps in doing so.
|